Understanding the
Role of Psychometric Testing in School Safety
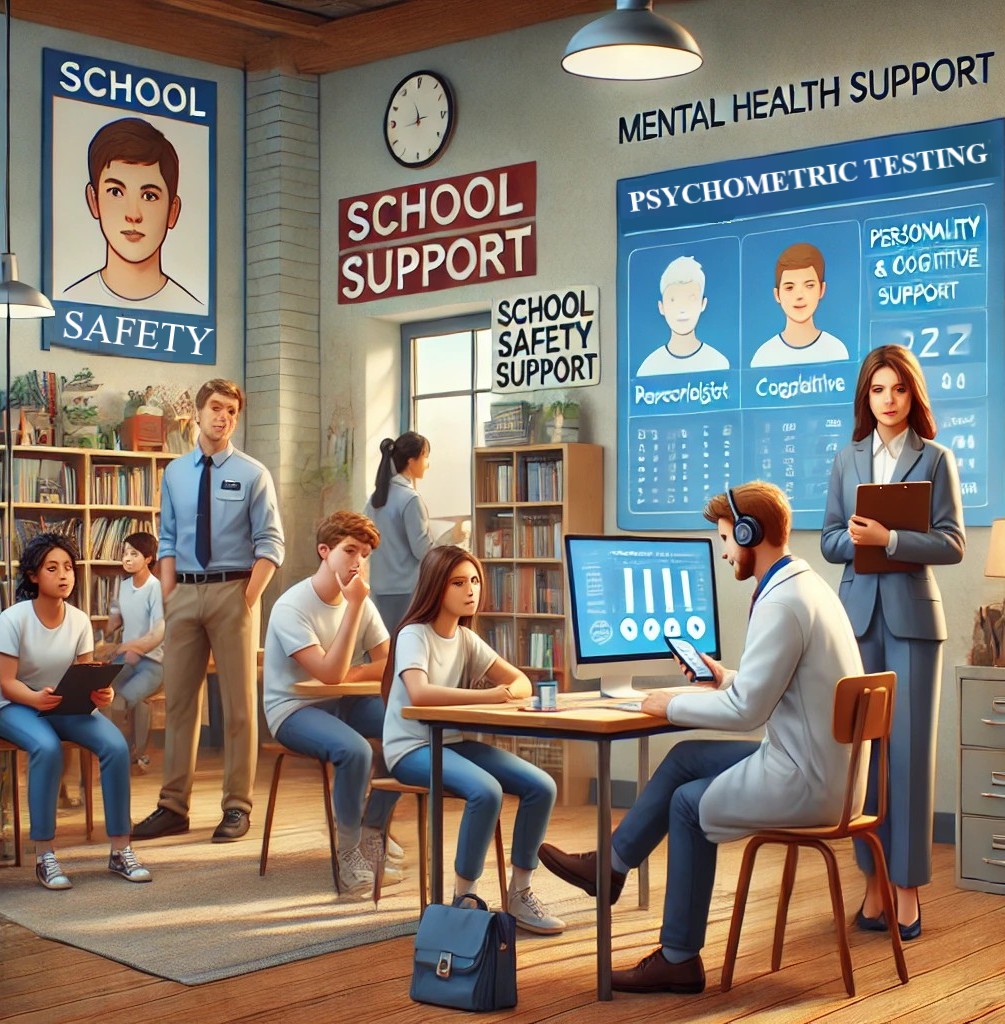
Definition and Purpose of Psychometric Testing
Psychometric testing
refers to standardized assessments designed to measure cognitive abilities,
personality traits, and behavioral tendencies. In the context of school safety,
these tests help identify students who may be at risk of emotional distress, aggressive
behavior, or other psychological factors that could contribute to school
violence. The primary purpose is to enable early intervention and create a
supportive school environment that prevents potential threats while fostering
student well-being.
The Evolution of School Safety Concerns
School safety has
evolved from concerns about physical security measures to include psychological
well-being and mental health interventions. In the past, schools relied on
metal detectors, security personnel, and surveillance cameras. However,
incidents of school violence, bullying, and self-harm have highlighted the need
for proactive approaches that address underlying psychological factors. This
shift has led to the integration of psychometric testing as a means to identify
at-risk students and intervene before issues escalate.
How Psychometric Testing Can Enhance School Safety
Psychometric testing
contributes to school safety by identifying behavioral risks, such as
aggression, anxiety, or emotional instability. These assessments provide
educators and mental health professionals with data-driven insights into
students' emotional and psychological states. By recognizing early warning
signs, schools can implement targeted interventions, counseling programs, and
personalized support to mitigate risks and enhance overall school safety.
Benefits and Challenges of Implementation
Benefits:
- Early identification of students
at risk for violence or self-harm.
- Data-driven insights that support
decision-making in mental health interventions.
- Reduction in bullying,
aggression, and behavioral conflicts.
- Improved student mental health
and emotional well-being.
Challenges:
- The potential for misdiagnosis or
false positives.
- Resistance from parents and
students due to privacy concerns.
- Ethical dilemmas in labeling
students based on test results.
- Cost and resource allocation for
implementation and follow-up interventions.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Concerns
Psychometric testing
in schools raises significant ethical and privacy concerns. Student data must
be handled with strict confidentiality, and informed consent from parents or
guardians is crucial. Additionally, there are concerns about how test results are
used and whether they could lead to stigmatization or discrimination. Schools
must establish clear policies on data storage, access, and usage to protect
student rights.
Case Studies from Schools Implementing Psychometric Testing
Several schools
worldwide have integrated psychometric testing into their safety strategies
with positive outcomes. For example:
- Case Study 1: A U.S. High School implemented
psychometric assessments to identify students at risk of depression and
aggression. Early intervention programs reduced disciplinary incidents by
40%.
- Case Study 2: A European School
District introduced personality and behavioral assessments, leading to
improved student counseling services and a decrease in school violence.
Expert Opinions on Its Effectiveness
Psychologists and
education experts generally support psychometric testing as a valuable tool in
school safety. However, they emphasize the importance of combining these tests
with other safety measures, such as counseling and behavioral interventions. Experts
also highlight the need for trained professionals to interpret results
accurately and implement appropriate interventions.
Future Trends in Psychometric Testing for Safety
The future of
psychometric testing in schools includes advancements in AI-driven assessments,
real-time behavioral monitoring, and integration with mental health support
systems. Emerging trends also focus on adaptive testing models that provide
personalized insights and recommendations for student well-being.